The Death of Freddie Gray and the Future of Police Reform Under Trump
Democracy in Crisis

Photo Credit: J.M. Giordano
On a cold and rainy day shortly after the election, I interviewed Baltimore Police Commissioner Kevin Davis in his office overlooking the city’s downtown. Donald Trump had just nominated noted racist Jeff Sessions as attorney general, and the consent decree the city had been negotiating with the federal government to reform its police department was in question.
“We lived through a George W. consent decree, [with a] Republican in the White House in Prince George’s County [in Maryland], and that consent decree lasted more than four years,” Davis said. “So anyone [who says] ‘With Republicans in the White House, consent decree is out the window,’ that’s not based on reality. So I expect we will have a consent decree. I expect it will be something we can work with.”
Trump, of course, is not just any Republican. And the consent decree, which was finally approved just before Trump took office, was almost out the window when Sessions asked a federal judge to halt the court’s approval of the agreement, having placed all consent decrees under review.
“I have grave concerns that some provisions of this decree will reduce the lawful powers of the police department and result in a less safe city," Sessions said earlier this month. "Make no mistake, Baltimore is facing a violent-crime crisis."
The city is in the midst of a murder crisis—318 murders in a population of just over 600,000 made 2016 the city’s second-most murderous year, after 2015, which saw 344 homicides—but Davis is clear that the consent decree will help, not hinder his attempts to fight violent crime. “We need a consent decree in Baltimore to fundamentally change this police department for decades to come,” he told me.
The Department of Justice began an investigation of the Baltimore Police Department before Freddie Gray’s death in police custody and the uprising that followed it in late April 2015—but the widespread unrest showed just how badly policing in the city was broken.
“[The police] come in, they move us, and they push us wherever they want to go,” a young man named Greg Butler told me of his decision to take to the streets after Freddie Gray’s funeral, when a CVS pharmacy was looted and set ablaze. “Today, we say, ‘We’re not moving.’ This has been claimed by the people of the city, police-free, because the police don’t know what they’re doing, and they’re not treating us right.”
In Baltimore, two years ago, there was almost a revolution. The riot on Apr. 27, 2015 was preceded by weeks of peaceful protests, where residents took to the streets, primarily in Baltimore’s poorest and most deeply segregated neighborhoods. In Sandtown, where Freddie Gray was arrested, residents referred to the police as an occupying army, a reality symbolized by the barricades placed around the Western District station, where officers in riot gear lined up with sticks and shields.
On Saturday, Apr. 25, the barricades broke out of Sandtown and came to the tourists. Fights broke out between protesters and sports fans drinking at bars outside of Camden Yards. A racist slur, a thrown beer, and suddenly it was chaos as punches, bottles and chairs were thrown. Kids took orange traffic cones and smashed out the windows of a police car, reaching inside, taking an officer’s hat, and wearing it.
Later that night, the police had revenge, away from the cameras—most of them, anyway.
When a line of riot cops wanted to snatch up a guy who had been yelling and shadow-boxing in front of them, they also beat on Baltimore City Paper photographer J.M. Giordano and arrested a Reuters photographer. Giordano got the shot as they dragged him across the ground: They were beating the shadow boxer with a billy club.
As the sun rose the next morning, National Guard trucks rolled into town as a weeklong curfew set in. For the next several nights, authorities tried to confine reporters to a pen in a corner near the protests.
These moments seem to prefigure our new reality now. If there was almost a revolution, Trump is the backlash. He did not create violent cops or angry sports fans—they created him. And instead of reigning in individual local cops, he wants to give them free reign. His policies will likely increase the dire poverty and segregation that account for so much crime. It’s hard to imagine another uprising where people do not die.
The patterns or practice report issued by the DOJ in August of 2016 was scathing, finding that the department regularly violated the civil rights of citizens, made unlawful stops and used excessive force. Mid-level commanders, brought up on the drug-war policies favored by Sessions, were noted as the worst offenders.
Still, it seems Sessions will gut the DOJ’s Civil Rights Division. Trump’s budget calls to cut the agency’s budget by more than $1 billion, and many expect much of that to come from civil rights enforcement.
Baltimore is the 14th Obama-era consent decree to go through—and it may be the last. And there’s still the danger that the Feds won’t sue for violations of the agreement.
It’s hard enough to win reform with people in the streets and a strong civil rights division in the DOJ. Without that, the police union and the law-and-order rhetoric of the president could be the loudest voices in a commissioner’s ear.
Keywords
More by Baynard Woods
-

With Much Love and Grim Solidarity, Democracy in Crisis Says Goodbye
Democracy in Crisis
-
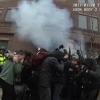
Trump Uses the Legal System for His Own Ends
Democracy in Crisis
-

A Mexican Reporter's Death Threats Are the Future of Journalism in America
Democracy in Crisis









comments